Mortgage REITs, or mREITs, provide real estate financing by originating or purchasing mortgages or mortgage-backed securities. They are an essential part of the residential mortgage market, helping to finance about 1 million homes in the United States each year. They also support the commercial real estate sector by providing loans to develop, acquire, reposition, and own income-producing properties.
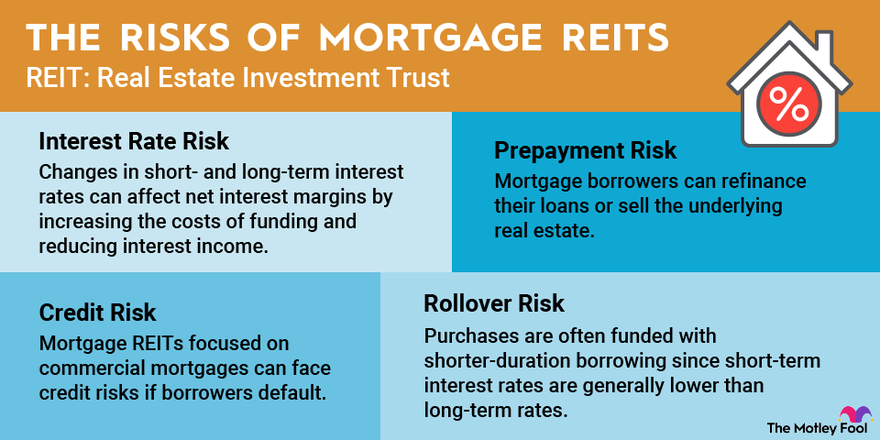
Image source: The Motley Fool.
Here’s a closer look at the overall mortgage REIT market and the sector’s unique risks. Plus, we’ll discuss a couple of interesting mREITs you might want to consider.
Understanding mortgage REITs
Understanding mortgage REITs
Mortgage REITs are a subcategory of the real estate investment trust (REIT) segment that focuses on real estate financing. The entities purchase or originate mortgages and mortgage-backed securities, earning interest income from their investments. Some mREITs also earn loan origination and servicing fees. These factors make mREITs similar to financial stocks.
Mortgage REITs make money differently than other real estate investments. They earn a profit on their net interest margin, which is the spread between the interest income generated by their mortgage assets and their funding costs. Mortgage REITs use various funding sources to originate and purchase mortgages and related securities. This can include common and preferred equity, repurchase agreements, structured financing, convertible and long-term debt, and credit facilities.
Mortgage REITs use those funding sources to acquire mortgage-related assets. Some mREITs will originate loans they hold on their balance sheet and sell them to other buyers, including government agencies, banks, or investors. In addition, mREITs purchase mortgages and mortgage-backed securities. They collect the fees and loan interest generated by mortgages, keeping what remains after paying funding and operating expenses.
Here’s an example of how mREITs work. Let’s say an mREIT raises $100 million of equity from investors to buy mortgages. It secures another $400 million in capital from other sources, at an average funding cost of 2%, allowing it to purchase $500 million of mortgage-backed securities.
If the loans had an average weighted yield of 3%, they would generate $15 million of interest income annually. Meanwhile, at a 2% cost of funding, it would have $8 million of annual funding costs, allowing the mREIT to generate $7 million of net interest margin each year.
IRS guidelines for mREITs require them to distribute 90% of net income to shareholders via dividend payments, which explains the high dividend yields for most mREITs.
Risks
Risks of investing in mortgage REITs
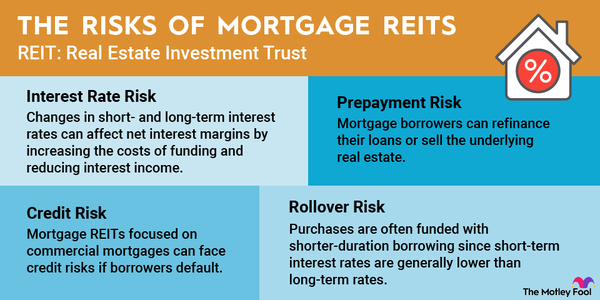
Mortgage REITs are riskier than many other investments, including other REITs, because they face certain specific risks, including:
- Interest rate risk: While changes in interest rates affect REITs overall, they have an even greater effect on mREITs because changes in short- and long-term interest rates can affect net interest margins by increasing the costs of funding and reducing interest income. Interest rate changes can also affect the value of an mREIT’s mortgage assets, impacting its net asset value and share price.
- Prepayment risk: Mortgage borrowers can refinance their loans or sell the underlying real estate. When that happens, it forces the mREIT to reinvest the repaid loan proceeds in the current interest rate market, which might be lower than the rate on the existing mortgage.
- Credit risk: Mortgage REITs focused on commercial mortgages can face credit risks if borrowers default. Mortgage REITs that focus on residential loans backed by government agencies don’t have to worry about this nearly as much.
- Rollover risk: Residential mortgage REITs tend to own long-term mortgages and mortgage-backed securities. However, they often fund these purchases with shorter-duration borrowing since short-term interest rates are generally lower than long-term rates. This funding strategy creates rollover risk. The mREIT must obtain funding at attractive rates to roll over loans as they mature.
2 best mortgage REITs
2 mortgage REITs to consider in 2025
There are several dozen mREITs, and many have underperformed the S&P 500 in recent years due to fluctuating interest rates. However, a couple of mREITs stand out as strong candidates in this volatile sector and could be worth a look for patient investors who want high income streams.
Here’s a closer look at these two leading mortgage REITs.
Arbor Realty Trust
Arbor Realty Trust is an mREIT that finances commercial real estate. It focuses on making loans backed by multifamily properties, single-family rentals, and land.
The real estate financing company has three business platforms:
- Balance sheet loan origination: Arbor underwrites loans that it holds on its balance sheet.
- Government-Sponsored Enterprise (GSE)/Agency loan origination: The REIT originates small-balance loans that it sells to Fannie Mae, Freddie Mac, the Federal Housing Administration, and other agencies.
- Servicing: Arbor provides servicing on multifamily loans primarily held by GSEs.
Arbor’s business model provides it with multiple income streams. The mREIT produces recurring long-dated cash flow from servicing fees, escrow revenue, and net interest income. It also generates one-time origination fees. This strategy gives it an advantage over mREITs solely focused on making money via the net interest margin.
Its diversified operating platform and multifamily focus have enabled it to generate fairly steady earnings in all market cycles. Arbor has delivered more than a decade of paying dividends at or above the previous quarter’s level. That’s notable since many mREITs have reduced their dividends in recent years because of the impact interest rates have had on their net interest margin.
AGNC Investment
AGNC Investment is an mREIT focused on investing in mortgage-backed securities protected against credit losses by government agencies like Fannie Mae, Freddie Mac, and Ginnie Mae. The REIT invests in mortgage-backed securities on a leveraged basis, primarily using repurchase agreements. It also uses a dynamic risk management strategy to protect the value of its portfolio from interest rate and other risks.
The REIT’s strategy has enabled it to pay a stable monthly dividend for the last several years. That dividend stability has made it stand out in a sector where many of its rivals have reduced their dividend payments as interest rates rose.
Related investing topics
Higher dividends with higher risk
Mortgage REITs offer higher dividends along with higher risk
Mortgage REITs can generate a significant net interest margin when there’s a wide spread between short-term interest rates (where they borrow) and long-term interest rates (where they lend). Unfortunately, the spread doesn’t usually stay wide for long, which is why mREITs tend to be very volatile.
Because of that risk, mREITs aren’t always the best option for income-seeking investors since their high yields fluctuate wildly. However, a couple of interesting mREITs are worth considering, as their differentiated business models help insulate them from the sector’s overall volatility.
FAQs
FAQs on Mortgage REITs
What are mortgage REITs?
Mortgage REITs are real estate investment trusts (REITs) that focus on owning mortgages and other loans backed by residential and commercial real estate. Instead of generating rental income from owning equity in a property, they collect interest income.
Are mortgage REITs worth investing in?
Mortgage REITs can be worth investing in. They typically invest in lower-risk loans backed by residential or commercial real estate. However, they often use leverage (i.e., debt and other capital sources) to boost their returns. That strategy can enable mortgage REITs to make a lot of money when the spread between their borrowing costs and the yields they earn on their investment is wide.
However, a narrowing of investment spreads, which typically occurs due to changes in interest rates, can significantly affect the returns these REITs earn. They tend to be riskier investment vehicles that often offer higher-yielding dividend payments that can fluctuate significantly.
How are mortgage REITs affected by interest rates?
Changes in interest rates impact both the borrowing costs of mREITs and the yields on their investments. For example, during a falling interest rate environment, borrowers will often refinance their loans. As a result, an mREIT will have to reinvest the repaid debt in the currently lower rate environment, causing its income to decline. Meanwhile, rising rates make it more expensive for an mREIT to borrow money to finance its existing portfolio.